|
The Journal of American Science
(J Am Sci)
ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264 (online),
doi prefix: 10.7537, Monthly
Volume 14, Issue 6, Cumulated
No. 124, June 25, 2018
Cover (jpg),
Cover (pdf),
Introduction,
Contents,
Call
for Papers,
am1406
You can use the message in end of the article abstract to
cite it.
To get Microsoft Documents: After you open the
"Full Text" for each article, change the last 3 characters of
the web address from .pdf to .doc
Welcome to send
your manuscript(s) to:
americansciencej@gmail.com.
CONTENTS
|
No.
|
Titles / Authors
|
Full
Text
|
No.
|
|
1
|
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic
Roles of BM-Mscs in Enhancing Pancreatic Auto-Immunity and
Apoptotic Status in TIDM
Wafaa M. El-Kholy1, Raza H. Hussein2 and Dlovan Y. Khalil2
1Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University,
Egypt
2Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Slymania University,
Kurdistan Iraq.
dlovanyasen@gmail.com
Abstract: Diabetes
mellitus (DM), a global health crisis, affecting humanity
regardless of the geographic location or socioeconomic profile
of the population, as it considered the principle cause of great
economic loss that can impede nation’s development. In recent
years; the transplantation of MSCs has achieved great
therapeutic effects in animal models due to their multipotency
along with their paracrine secretion of cytokines, angiogenic
and neurotrophic factors, angiogenic factors, anti-inflammatory
effects and immunomodulatory substances. Therefore, the current
study was designed to assess the probable antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory, immuno-suppressive and anti-apoptotic
protective capacities of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem
cells (BM-MSCs) in comparison with insulin treatment in diabetic
rats. Animals were divided into four groups; control group,
diabetic group (D) which received a single intraperitoneal STZ
dose (45 mg/kg b.w), D + insulin (0.75 IU/ 100 gm b.w., daily)
group and D + BM-MSCs (single intravenous dose of 10 6
cell/rat); and the study continued for four consecutive weeks.
Obtained results showed that either insulin or BM-MSCs
administration remarkably improve the oxidative stress status
resulting from diabetes induction; as reflected by lowered
pancreatic MDA, ROS and XO levels; and enhanced the antioxidant
defense system capability via increasing pancreatic contents of
GSH, SOD, CAT, GST and TAC, compared to the diabetic group.
Also, treatment of diabetic rats with insulin or BM-MSCs
significantly ameliorated the inflammatory disorders as
indicated by markedly decreased serum inflammatory markers; such
as CRP, TNF-α, TGF-β and CD 95; compared to the untreated
diabetic rats. In addition, insulin or BM-MSCs therapy was found
to suppress pancreatic auto-immunity resulting in an obvious
pancreatic cells apoptosis arrest in diabetic rats; which was
confirmed by declined pancreatic CD4+, CD8+, annexin, P53 and
caspase-3 levels accompanied by BCl-2 level elevation; compared
to the diabetic group. Current findings provided additional
evidence that BM-MSCs therapy has antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and anti-apoptotic
characteristics which may greatly ameliorate diabetic patients'
health through minimizing various DM side effects.
[Wafaa M. El-Kholy, Raza H. Hussein and Dlovan Y. Khalil.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Roles of BM-Mscs
in Enhancing Pancreatic Auto-Immunity and Apoptotic Status in
TIDM. J Am Sci 2018;14(6):1-12]. ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN
2375-7264 (online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org. 1.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.01.
Key words: Antioxidant –Apoptosis – BM-MSCs – Diabetes –
Inflammation –Oxidative stress– Streptozotocin |
Full Text |
1
|
|
2
|
The Protective Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived
Mesenchymal Cells on Nephrotoxicity Induced by Carbone
Tetrachloride in Adult Male Albino Rats: Histological and
Ultrastructural Study
Eman E. Elwakeel1*, Amira Z. Mohamed 2
1Anatomy and Embryology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Benha
University, Benha, Egypt
2Microbiology, Electron Microscopic Unit, Faculty of Medicine,
Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt.
E-mail: eman.ismail@fmed.bu.edu.eg;
elwakeelazs@gmail.com
Abstract:
Background: Exposure to carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) initiates
nephrotoxicity in rats. The purpose of the present work was to
study the role of bone marrow- derived mesenchymal cells (BM-MSCs)
on CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in adult male albino rat judged
by light and electron microscopeusing histological,
immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure parameters. Material &
methods: Thirty adult male albino rats were classified randomly
into four experimental groups. Group I: Control group which was
equally divided into two subgroups; Ia (thatwas fed on the
standard diet) and Ib (that injected intraperitoneally with 0.1
ml of olive oil twice weekly for 4 weeks ). Group II: treated
with 1.0ml /kg b.w of 10% CCl4 dissolved in olive oil, IP, twice
a week for 4 one month. Group III: was injected intraperitonealy
with the same dose of CCl4 twice a week for 4 weeks and then
were given a single dose intraperitoneally of 3×106 BM-MSCs.
Group IV: served as recovery group, were treated IP with 5.0ml
/kg b.w of 10% CCl4 twice a week for 4 weeks and left for a
further 4 weeks. At the end of experimental period, all of the
rats were scarified and both kidneys were prepared for
histological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study.
Results: In CCl4treated animals, there were several pathological
changes included: dilatation of tubular lumens with intraluminal
cell debris and vacuolation of tubular epitheliumas compared
with the control rats. Mallory’s trichrome staining showed
increased amount of collagen fibers in the glomerulus and
interstitium in CCl4 treated animals. While the rest of groups
showed minimal collagen fibers around glomerulus and renal
tubules. Immunohistochemical staining using α-Smooth muscle
actin (α-SMA) showed negative reaction in all groups except CCl4
treated animals and recovery group. EM evaluation of CCL4
induced changed revealed significant condensation of chromatin
in the nucleus and shortened brush border of proximal convoluted
tubules, swollen mitochondria and loss of apical plasma membrane
micro projection of distal convoluted tubules, also effacement
of secondary foot processes on basement membrane of glomerular
capillary with loss of slit diaphragms. In contrast, these
deleterious histopathological alterations resulting from
CCl4nephrotoxin were absent after BM-MSCs treatment in CCl4 +
BM-MSCs group of rats. Conclusion: Our results demonstrated the
protective potential of BM-MSCs on CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity
in adult male albino rat with better recovery findings in BM-MSCs
received group than in those rats that were left to recover
without treatment.
[Eman E. Elwakeel, Amira Z. Mohamed. The Protective Effect of
Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Cells on Nephrotoxicity Induced
by Carbone Tetrachloride in Adult Male Albino Rats: Histological
and Ultrastructural Study. J Am Sci 2018;14(6):13-24]. ISSN
1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264 (online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
2. doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.02.
Keywords: Carbon tetrachloride; bone-marrow; renal
dysfunction; nephrotoxicity; stem cell. |
Full Text |
2
|
|
3
|
A Morphologic and Morphometric Study of the
Foramen Transversarium of the Cervical Vertebrae: An
Osteological Study in Upper Egypt
Salwa M. Ouies
Lecturer of Human Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine,
Sohag University, Egypt.
salwaouies@yahoo.com
Abstract:
Introduction: The Knowledge of variations in foramen
tranversarium of the cervical vertebrae is surgically important,
as its anatomical relation with the third part of vertebral
artery is one of the proposed causative factors for cervicogenic
headache. Aim of work: This study was aimed to determine the
morphological and morphometrical variations of foramen
transversarium (FT) of cervical vertebrae in Upper Egypt.
Methods:100 cervical vertebrae were collected from Anatomy
department of medical College of Sohag and Assiut universities.
Each vertebra was examined for the shape of foramen
tranversarium and their dimensions were measured. Any other
variation observed was also noted. Results were statistically
analysed for side and size variation. Results: The foramen
transversarium take one of 5shapes: rounded, oval with more AP
diameter, oval with more transverse diameter, elliptical and
triangular. There were no significant differences between the
right and left as regard the antroposterior and transverse
diameters Conclusion: Morphological variations in foreman
transversarium are significant as they lead to neurological
conditions due to the flow of blood passing through these
openings except for C7.
[Salwa M. Ouies. A Morphologic and Morphometric Study of the
Foramen Transversarium of the Cervical Vertebrae: An
Osteological Study in Upper Egypt. J Am Sci 2018;14(6):25-29].
ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264 (online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
3. doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.03.
Keywords: Upper Egypt, Cervical vertebra, Foramen
transversarium |
Full Text |
3
|
|
4
|
Design and Implementation of Employee Computer
Usage Behavior System (5 May 2015)
1Ainee Riaz, 2Shahid Islam
1 Research Scholar, University of Engineering and Technology
Lahore, Pakistan
E-Mail: Ainee_riaz@yahoo.com Phone no: +923016543211
2 Assistant Professor, University of Engineering and Technology
Lahore, Pakistan (Computer Science Department)
Abstract—The
proliferation of software applications has great impact on our
lives. It not only saves the time but also makes the life
easier. The aim of this research is to design and develop a
software application that could help the managers to maximize
the office productivity by monitoring the computer activities of
each employee. This system provides the server application that
logs the employees’ computer usage and archives them at central
server. Authorized users like managers can retrieve this
information like web history, printer usage, installed
applications, running programs etc from server using web based
interface.
[Ainee Riaz, Shahid Islam. Design and Implementation of Employee
Computer Usage Behavior System (5 May 2015). J Am Sci
2018;14(6):30-37]. ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org. 4.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.04.
Keywords— employees, computer usage, monitoring, system |
Full Text |
4
|
|
5
|
Study the interaction of cultivation
date and variety on the process of changes dry
weight of
the leaves, stems,
clusters and
flower, rice varieties on the date of winter
and summer
cultivation in Khuzestan
Fazollah
Hooshmand
PhD
student of Agriculture
Engineering at
the Islamic Azad
University, Science & Research
Khuzestan-Ahvaz
faz.hooshmand@yahoo.com
Abstract:
This research conducted for
determination the rate and process of dried matter variation of
plant
organ rice varieties in summer and winter planting of Khuzestan
as split-plot design in randomized complete blocks with two
factors (planting date and variety) and three replication for
one year (2009) in Shavoor Agriculture Research Station related
to Natural Resources and Agriculture Research Center of
Khuzestan with eastern length 48:28 m and northen width 31:50 m.
The main factor in three levels, included date of cultivation
2009/3/17 (D1), 2010/4/14 (D2) and 2010/5/26 (D3) and rice
varieties namely Hoveizeh (V1), Hamar (V2),
Ramhormoz pollen (V3), Dollar (V4), N22
(V5), Zanjan pollen (V6), Eiry 3 (V7)
Eiry 12 (V8), line7 (V9), Line 13 (V10) were examined
as subplot.
In this experiment, native and Khouzestan heat tolerance variety
like Hamr with high growth duration and more tillering rate had
the highest process of leaf dried matter, stem, total, and there
is positive correlation among them (at level 1%). Tolerance and
native varieties had the most suitable variations process of
these indexes in every three dates of planting. In first and
second date of planting, not produced remarkable fertile
panicles because of exposing panicle with severe hot weather in
July, Therefore they produced dried matter lower than third date
of planting.
[Fazollah Hooshmand.
Study the interaction of
cultivation date and variety on the process of
changes dry weight
of the
leaves, stems,
clusters and flower, rice
varieties on the date of winter
and summer
cultivation in Khuzestan.
J Am Sci
2018;14(6):38-44].
ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online).
http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
5.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.05.
Key words:
Interaction, Date of planting, variety, changing process, Dried
matter |
Full Text |
5
|
|
6
|
Causes of Employees turnover
in banking sector of Pakistan
Muhsin Bilal1,
MISS Muqdas Rehman2,
Chaudhary Abdul Rehman3
1PHD
Scholar, Superior University, Lahore
Contract: 0342-0656493, Email:
mohsinbilalncn@yahoo.com
2Lecturer,Hailey
College of Commerce, Punjab University,Lahore
Contact: 042-9231274 Email:
iluvnabi.saaw@gmail.com
3Professor,
Business School, superior University, Lahore
Contact: 042-35530361-8 Email:
ceo@superior.edu.pk
Abstract: Purpose:
Employee’s turnover is considering very important elements in
every country economy. The country of higher employee’s turnover
is live complex environment every time. This study aims to
determine the factors which are created the high employee
turnover. The job satisfaction, promotion, salary package,
organization commitment, workload balance appreciation of work,
employees training and development, organizantal culture and
workforce is very important factor in employee’s turnover in
Pakistan. This research provides complete guideline and
directions how job satisfaction, promotion, salary package,
organization commitment, workload balance and appreciation of
work will affect the employee turnover.
Methodology:
Data was collected through interview only Narowal district banks
of Pakistan. This study analyze that there is positive
relationship between employee turnover and factors which affects
them. Those banks which provide friendly environment, job
satisfaction, fulfill their commitments, workload balance and
promotion their employees is more satisfy them then those which
do not fulfill these factors. Findings: The finding of
the research is beneficial for the management of those banks in
which employee are not satisfy and leave the jobs very soon when
they are find a new one. Envivo software is used for discussion
and analysis.
Limitation: The
limitation of the study is that we only focus the banks of
district narowal and choose the data collection method is only
for interview and due the busy management in those banks they
have not in a position to answer me all of my question.
[Muhsin
Bilal, MISS Muqdas Rehman, Chaudhary Abdul Rehman.
Causes of Employees
turnover in banking sector of Pakistan.
J Am Sci
2018;14(6):45-54].
ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online).
http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
6.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.06.
Key words:
job satisfaction, promotion, salary package, organization
commitment, workload balance, appreciation of work, employees
training and development, Organizational culture and workforce |
Full Text |
6
|
|
7
|
Adaptive Routing Algorithms based Fault-tolerant
in 3D NOC
*Mohammad Trik1,2, Fardin Mohammadi Darvandi1,2, Kumarth nazari3
1,2Young Researchers and Elite Club, Sardasht Branch, Islamic
Azad University, Sardasht, Iran
1,2Young Researchers and Elite Club, Urmia Branch, Islamic Azad
University, Urmia, Iran
3 Applied Science Training Center of Justice Kermanshah,
Kermanshah, Iran
*Author for Correspondence
Abstract: In
traditional congestion aware techniques, congestion is measured
at a router level and delivered to other routers, either local
or non-local. In this work, we present an efficient fully
adaptive fault-tolerant routing algorithm for 3D Network-on-Chip
(3D NoC). The presented approach is discussed in both
two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) mesh networks.
To collect and propagate the congestion information of different
clusters, a distributed approach is presented. Instead of
rerouting packets around the fault regions when fault occurs,
our proposed algorithm applies a fault detection scheme which
can get the fault information one hop away in advance, and it
combines the fault information when doing the path computation.
This algorithm can deal with multi faults in the 3D NoC
architecture. Simulation results show that our proposed routing
algorithm can achieve lower latency, energy consumption and
higher packet arrival rate compared with other traditional
routing algorithms in various network applications.
[Mohammad Trik, Fardin Mohammadi Darvandi, Kumarth nazari.
Adaptive Routing Algorithms based Fault-tolerant in 3D NOC. J Am
Sci 2018;14(6):55-59]. ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org. 7.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.07.
Keywords: fault-tolerant, routing algorithm, adaptive, 3D
NoC |
Full Text |
7
|
|
8
|
[J Am Sci
2018;14(6):60-66].
ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online).
http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
8.
withdrawn |
Full Text |
8
|
|
9
|
Percutaneous Coronary
Revascularization Versus Surgery In Multi-vessel Disease
Mohamed Mahmoud*, Osama Osman**,
G.M. Shaaban***, M.M. Nasr*****
Al-Azhar Assiut University
Cardiology departments (*, **), Cardiology National Heart
Institute and Cardiothoracic Surgery National Heart Institute
(***, ****)
mrefatyusuf@gmail.com
Abstract:
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) remains the leading cause of
mortality in the world. It presents as a spectrum of diseases
and syndromes ranging from asymptomatic quiescent states to
sudden cardiac death (SCD). When it manifests as obstructive
coronary artery disease (CAD), it typically presents as angina
pectoris or myocardial infarction (MI).
Although mortality has improved over the past several decades,
the increasing burdens of obesity, diabetes, and an aging
population challenge health care systems and populations. Many
treatments have been linked to the improvement of mortality from
CAD. These include secondary preventive medical therapy and
revascularization; initial treatments for acute coronary
syndromes (ACS), including ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI);
revascularization for chronic angina; treatment for heart
failure (HF); and primary preventive therapies, including
treatment of hypertension (HTN) and hyperlipidemia. Multivessel
coronary artery disease (MVCAD) is characterized by involvement
of greater than 1 epicardial coronary artery (CA) or the
unprotected left main (LM). The choice of revascularization
strategy in this setting remains a critical issue in cardiology.
Although coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) has
traditionally been the revascularization strategy for most
patients with MV disease, there has been a gradual shift toward
percutaneous revascularization (PCI). Early randomized clinical
trials showed CABG to be superior to medical therapy. However,
trials comparing CABG to bare metal stenting have not shown a
mortality benefit. Advancements in interventional techniques
will continue to challenge the notion that CABG is the standard
therapy for patients with MVCAD. Several ongoing randomized
clinical trials comparing CABG to drug eluting stents (DES) will
provide valuable insight into the role of each procedure.
Limited data suggests that CABG is superior to MV PCI even when
drug-eluting stents are used. Several ongoing randomized trials
are evaluating the long-term comparative efficacy of PCI with
DES and CABG in patients with DM.
Significant LM CAD is characterized as angiographic stenosis of
≥50% of this segment of the coronary tree. It is found in 2.5%
to 10% of all patients undergoing diagnostic coronary
angiography procedures. Though CABG is currently the gold
standard for revascularization of patients with unprotected LMCA
stenosis, stent implantation in carefully selected patients
appears to be both feasible and safe. Many
cardiologists consider it reasonable to assume that PCI
using DES thought to be considered equivalent, if not
superior to CABG. The argument made is that in
previous randomized clinical trials comparing PCI to
CABG, restenosis was
the determining factor favoring surgery, an event
that clinical experience suggests is no longer as frequent.
In the absence of a definitive clinical trial to support
this view, how should the prudent, cutting edge
cardiologist evaluate the data and manage their
patients. Aim of the Work: The purpose of
this study is to compare the safety and efficacy of PCI using
Drug Eluting Stents versus CABG in treatment of MVCAD.
Patients and methods 1-Patients: This study was
conducted on 50 patients with IHD in the Cardiology departments
of National heart Institute from April 2011 to August 2012. 25
of them will undergo PCI using DES while the other 25 will
undergo CABG. All patients underwent diagnostic coronary
angiography which showed MV lesions with good distal run off
that could be treated either by PCI or CABG. The patients
were divided into two groups: 1-Group (A) included 25
patients who underwent PCI to accessible lesions. 2-Group (B)
included 25 patients who underwent CABG for diseased vessels.
Inclusion Criteria: Patients were included if they: Have
MV CAD, manifested by -Typical chest pain or angina equivalent -ECG
changes suggesting CAD -Wall motion abnormalities by echo if
present. Exclusion Criteria: -Patients
were excluded if they are: - 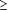 80
years of age -Severely impaired LV function -Have less than
3vessel disease -Have prior revascularization procedures. -Have
experienced an acute MI within 24 h before the
procedure. – Multi-organ dysfunction Methods: All
patients will be subjected to 1-informed consent 2- full history
taking 3-Full clinical examination 4-12-lead ECG pre and post-
intervention. 5- Full Conventional
transthoracic Echocardiograpgy (TTE) before the
intervention with a re assessment after 6 and 12 months. 6-
Dobutamine stress echo or thallium study before and after the
procedure to assessment of ischemic myocardium. 7- Coronary
angiography A detailed discussion with the patient and his
family about benefits of coronary angiography, methods for
revascularization, and possible complications was done. Informed
consent was signed by the patient after his approval of the
procedure. All patients underwent CABG: All these
patients provided a written consent; the protocol and the
consent were consistent with the national heart institution
protocols. Patients were treated with the intention of achieving
complete revascularization of all vessels at least 2.5 mm in
diameter with stenosis of 70% or more as identified by local
interventional cardiologists and cardiac surgeons. The surgical
technique for CABG, approaches used for stent implementation and
the post procedure medication regimen were chosen according to
local clinical practice. Follow-up Protocol:
(A) In hospital follow up: Patients
were followed up during hospital stay after revascularization
for: i. Mortality: ii. Morbidity. iii. Need for
revascularization. Iv. Occurrence of any neurological or
vascular events. V. Others. Duration of hospital stay was
documented in the medical record of each patient. (B)Outpatient
six months follow up: For all patients
the following was done: 1-Duration of stay at home and ability
to return to work. 2- Close observations of all the patients and
detailed history taking for early detection of any major adverse
cardiac events (MACE) including: 1-All causes of SCD 2-
Unstable angina or MI, diagnosed by: A. Appearance of any
symptoms or signs of acute chest pain. B. New ECG changes (ST-T
wave changes and pathological Q wave). C. Elevated cardiac
enzymes. iii. Need for revascularization whether surgical or
PCI. Echo for detection of any change in LVEDD, LVESD,
LVPW, IVS thickness and EF. (C)Outpatient 12months
follow up: For all patients the
following was done: as done before with six months follow up
Statistics: All the
data obtained were analyzed statistically using statistical
package,
Results:
Follow up for one year for all the patients showed that MACE
positive patients in group (A) were 36% occurred at
9.78±2.1 months. No
mortality was found during that period. On the contrary, group
(B) showed 24% MACE positive patients, 8% mortality. All our
complications occurred during post procedure hospital stay.
The difference between the two groups was statistically
insignificant. A
Combination of semiquantitative stress echo and the clinical
history allows us to define the risk of all late cardiac events
for patients with MVD undergoing stenting or surgery. This study
demonstrates that dobutamine stress echo is a powerful predictor
of late cardiac event after coronary revascularization and is
superior to simple clinical risk assessment. Regarding
group (A), duration of DM was significant predictor of in-stent
restenosis (ISR). Mean duration of DM in MACE
positive patients was 18.1±7.39 years, versus 10.93±6.38 years
in MACE negative patients. Difference between the two groups was
statistically significant.
In comparison, group (B) showed mean duration
of DM in MACE positive patients was 10.17±3.25 years, versus
10.53±4.89 years in MACE negative patients. Difference between
the two groups was statistically insignificant. Regarding group
(A), Insulin therapy was statistically significant predictor of
ISR. Treatment of DM in MACE positive patients was insulin in 6
patients (67%) and insulin with oral hypoglycemic agents in 3
patients (33%). on the other hand treatment of DM in MACE
negative patients was insulin in 6 patients (38%) and oral
hypoglycemic agents in 10 patients (62%). Difference between the
two groups was statistically significant. In comparison, group
(B) showed treatment of DM in MACE positive patients was insulin
in 2 patients (33%) and oral hypoglycemic agents in 4 patients
(67%). on the other hand treatment of DM in MACE negative
patients was insulin in 4 patients (21%), oral hypoglycemic
agents in 12 patients (63%) and both in 3 patients (16%).
Difference between the two groups was statistically
insignificant. Regarding group (A), stent length and number was
not a predictor of ISR.
Also in group (B) type of the graft did not affect the
clinical outcome. 80
years of age -Severely impaired LV function -Have less than
3vessel disease -Have prior revascularization procedures. -Have
experienced an acute MI within 24 h before the
procedure. – Multi-organ dysfunction Methods: All
patients will be subjected to 1-informed consent 2- full history
taking 3-Full clinical examination 4-12-lead ECG pre and post-
intervention. 5- Full Conventional
transthoracic Echocardiograpgy (TTE) before the
intervention with a re assessment after 6 and 12 months. 6-
Dobutamine stress echo or thallium study before and after the
procedure to assessment of ischemic myocardium. 7- Coronary
angiography A detailed discussion with the patient and his
family about benefits of coronary angiography, methods for
revascularization, and possible complications was done. Informed
consent was signed by the patient after his approval of the
procedure. All patients underwent CABG: All these
patients provided a written consent; the protocol and the
consent were consistent with the national heart institution
protocols. Patients were treated with the intention of achieving
complete revascularization of all vessels at least 2.5 mm in
diameter with stenosis of 70% or more as identified by local
interventional cardiologists and cardiac surgeons. The surgical
technique for CABG, approaches used for stent implementation and
the post procedure medication regimen were chosen according to
local clinical practice. Follow-up Protocol:
(A) In hospital follow up: Patients
were followed up during hospital stay after revascularization
for: i. Mortality: ii. Morbidity. iii. Need for
revascularization. Iv. Occurrence of any neurological or
vascular events. V. Others. Duration of hospital stay was
documented in the medical record of each patient. (B)Outpatient
six months follow up: For all patients
the following was done: 1-Duration of stay at home and ability
to return to work. 2- Close observations of all the patients and
detailed history taking for early detection of any major adverse
cardiac events (MACE) including: 1-All causes of SCD 2-
Unstable angina or MI, diagnosed by: A. Appearance of any
symptoms or signs of acute chest pain. B. New ECG changes (ST-T
wave changes and pathological Q wave). C. Elevated cardiac
enzymes. iii. Need for revascularization whether surgical or
PCI. Echo for detection of any change in LVEDD, LVESD,
LVPW, IVS thickness and EF. (C)Outpatient 12months
follow up: For all patients the
following was done: as done before with six months follow up
Statistics: All the
data obtained were analyzed statistically using statistical
package,
Results:
Follow up for one year for all the patients showed that MACE
positive patients in group (A) were 36% occurred at
9.78±2.1 months. No
mortality was found during that period. On the contrary, group
(B) showed 24% MACE positive patients, 8% mortality. All our
complications occurred during post procedure hospital stay.
The difference between the two groups was statistically
insignificant. A
Combination of semiquantitative stress echo and the clinical
history allows us to define the risk of all late cardiac events
for patients with MVD undergoing stenting or surgery. This study
demonstrates that dobutamine stress echo is a powerful predictor
of late cardiac event after coronary revascularization and is
superior to simple clinical risk assessment. Regarding
group (A), duration of DM was significant predictor of in-stent
restenosis (ISR). Mean duration of DM in MACE
positive patients was 18.1±7.39 years, versus 10.93±6.38 years
in MACE negative patients. Difference between the two groups was
statistically significant.
In comparison, group (B) showed mean duration
of DM in MACE positive patients was 10.17±3.25 years, versus
10.53±4.89 years in MACE negative patients. Difference between
the two groups was statistically insignificant. Regarding group
(A), Insulin therapy was statistically significant predictor of
ISR. Treatment of DM in MACE positive patients was insulin in 6
patients (67%) and insulin with oral hypoglycemic agents in 3
patients (33%). on the other hand treatment of DM in MACE
negative patients was insulin in 6 patients (38%) and oral
hypoglycemic agents in 10 patients (62%). Difference between the
two groups was statistically significant. In comparison, group
(B) showed treatment of DM in MACE positive patients was insulin
in 2 patients (33%) and oral hypoglycemic agents in 4 patients
(67%). on the other hand treatment of DM in MACE negative
patients was insulin in 4 patients (21%), oral hypoglycemic
agents in 12 patients (63%) and both in 3 patients (16%).
Difference between the two groups was statistically
insignificant. Regarding group (A), stent length and number was
not a predictor of ISR.
Also in group (B) type of the graft did not affect the
clinical outcome.
[Mohamed
Mahmoud Osama Osman G.M. Shaaban M.M. Nasr.
Percutaneous Coronary
Revascularization Versus Surgery In Multi-vessel Disease.
J Am Sci
2018;14(6):67-83]. ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264
(online).
http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
9.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.09.
Keywords:
Percutaneous; Coronary; Revascularization; Versus; Surgery;
Multi-vessel Disease |
Full Text |
9
|
|
10
|
The therapeutic effect of some tuber plants that
found in the Al- Baha area on bio-chemical changes in
hyperglycemic rats
Dr. Lobna Saad Mohammed Abd Elmeged1, Dr. Nora Mesfer Attia Al
zahrani2
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Home Economics, Faculty of
Sciences and Arts, Al Baha University-KSA
2 Associate Professor, Department of Home Economics, Faculty of
Science and Arts, Al Baha University- KSA
lobna_lolo_2007@yahoo.com
Abstract:
Background: Leafy vegetables are among the most nutritious
vegetables on a fresh weight basis and are also among the
world's most productive plants in terms of nutritional value per
unit area, in part because they grow rapidly, allowing several
crops or harvests in a season Objective: This investigation aims
to therapeutic effects of vegetable growths (green onground
parts) of tuberous plants such as greens of taro, carrot, suger
beet, sweet potato, and potato leavesand stem are scant. Design:
Thirty-five rats Sprague Dawley white male albino rats, weighing
about 150 ± 10g were used in the study. The experiment was
performed in Animal House. All rats were fed for one week on
basal diet before starting the experiment, then divided into two
main groups, the first group (n= 5 rats) was fed on the basal
diet only as a control negative (C –ve) normal rats for 28 days.
The rats of second main group (n= 30 rats) were injected alloxan.
The obtained data were statistically analyzed using computerized
SPSS Results: Hyperglycemic rats fed on taro, carrot, sugar
beet, sweet potato, and potato leaves and stems 5% recorded
significant decrease in Serum GPT compared to control (+ve)
Hence there was a significant increase in control (+) compared
to control (-) rats. Diabetic rats fed on taro, carrot, sugar
beet, sweet potato and potato leaves and stems 5 % denoted
significant decreases in serum glucose compared to control (+)).
Diabetic rats fed on taro, carrot sugar beet, sweet potato and
potato leaves and stems 5% diet denoted significant decreases in
U.acid compared to control (+ve) rats, Recommendation: This
study suggested to use vegetable greens of tuberous plants,
namely that of taro, carrot, sugar beet, sweet potato and potato
for hyperglycemic patients
[Lobna Saad Mohammed Abd Elmeged, Dr. Nora Mesfer Attia Al
zahrani. The therapeutic effect of some tuber plants that found
in the Al- Baha area on bio-chemical changes in hyperglycemic
rats. J Am Sci 2018;14(6):84-95]. ISSN 1545-1003 (print); ISSN
2375-7264 (online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org. 10.
doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.10.
Keywords: vegetable greens of tuberous plants, Diabetic,
Biochemical change |
Full Text |
10
|
|
11
|
Phytochemical and Therapeutic Studies of
the Fruit Essential Oil of Thuja orientalis from Nigeria
Ololade Z.S.1*, Fakankun O.A.1, Alao, F.O.2, Udi O.U.1
1Department of Chemical Sciences, Bells University of
Technology, P.M.B. 1015, Ota, Nigeria
2Department of Biological Sciences, Bells University of
Technology, P.M.B. 1015, Ota, Nigeria
zacchsnatpdt@gmail.com;
suntolgroup@yahoo.com
Abstract: The aim of this study was to
establish correlations between the identified phytocompounds in
the fruit essential oil of Thuja orientalis from Nigeria and
their medicinal properties (free radical scavenging, antioxidant
and antimicrobial). Forty-seven compounds were identified in the
fruit essential oil of T. orientalis making up 98.9% of the
total percentage composition. The essential oil was made up
predominantly of monoterpenoids (62.2%). The most abundant
components was 1R-α-pinene (15.2%) followed by α-pinene (9.6%),
1S-α-pinene (5.6%), cyclofenchene (5.6%), (+)-3-carene (4.5%),
6,6-dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo [3.1.1] heptane (4.5%) and
trans-β-ocimene (4.0%). The high amount of terpenoids leads to
more potent radical scavenging, antioxidant and antibiotic
properties. The essential oil showed high potential as natural
antioxidant and free radical inhibitor with IC50 value:
2.5µgml-1, the percentage inhibition of free radical ranged
between 68-70%. Screening of the fruit essential oil for
antimicrobial activities using the agar-well diffusion assay
showed that the oil had high antibacterial properties against
all bacteria isolates tested with zones of inhibition ranging
from 10-30 mm. This study confirms that the fruit essential oil
of this plant contains phytochemicals that can form the basis
for the development of a potential natural antioxidant and
antibiotic which are safe, cheap, and readily available at a
large scale for pharmaceutical industries for further
investigation and processing.
[Ololade Z.S., Fakankun O.A., Alao, F.O., Udi O.U. Phytochemical
and Therapeutic Studies of the Fruit Essential Oil of Thuja
orientalis from Nigeria. J Am Sci 2018;14(6):96-100]. ISSN
1545-1003 (print); ISSN 2375-7264 (online). http://www.jofamericanscience.org.
11. doi:10.7537/marsjas140618.11.
Keywords: Thuja orientalis, fruit essential oil,
phytochemical, antioxidant, antibacterial |
Full Text |
11
|
The
manuscripts in this issue are presented as online first for
peer-review, starting from
June 10, 2018.
All
comments are welcome:
editor@americanscience.org;
americansciencej@gmail.com,
or contact with author(s) directly.
For back issues of the Journal of American Science, click here.
Emails:
editor@americanscience.org;
americansciencej@gmail.com
|